- About
- Glass
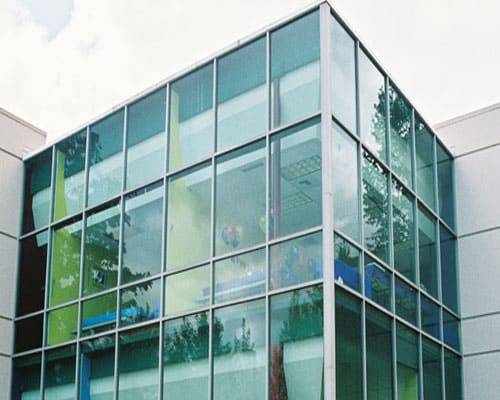
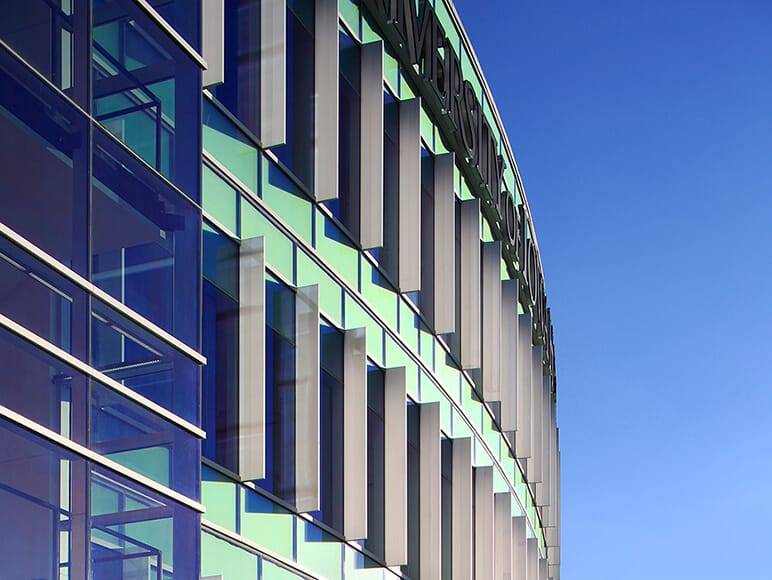
Glass overview
- Glass Options
- Specialty Glass Options
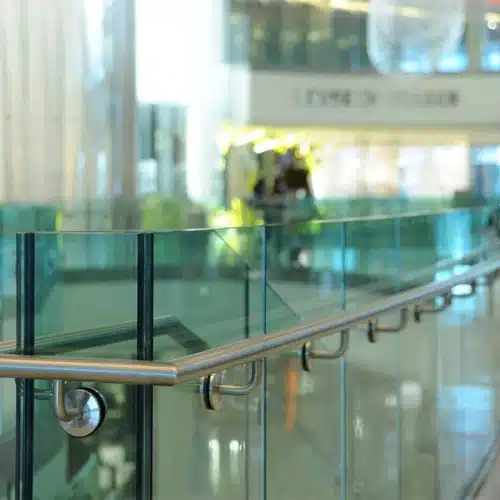
- Glass Balustrades
- Solutions
Heat strengthened glass is a similar process to tempering glass.
When it comes to security in commercial settings, tempered glass installation is a top choice.
Laminated glass is a versatile glazing option that offers a wide range of benefits.
Insulated glass units are 2 or more panes of glass made into one unit.
Low E coatings are a major factor in the performance of a sealed unit.
Single-glazed solution is a popular and versatile glazing solution widely used in various applications.
Double-glazed solution is a revolutionary solution offered by Unique Glass and Aluminum Solutions.
Triple glazed solution is at the forefront of energy-efficient building design.
Translucent glazing solutions offer a versatile and visually appealing option for glass surfaces.
Acoustic glazing solutions offer an effective way to mitigate noise transmission through glass.
Heat Strengthened GlassHeat strengthened glass is a similar process to tempering glass.
Acid Etched GlassAcid-etched glass is a highly sought-after glazing option that offers a perfect blend of privacy, aesthetics, and functionality.
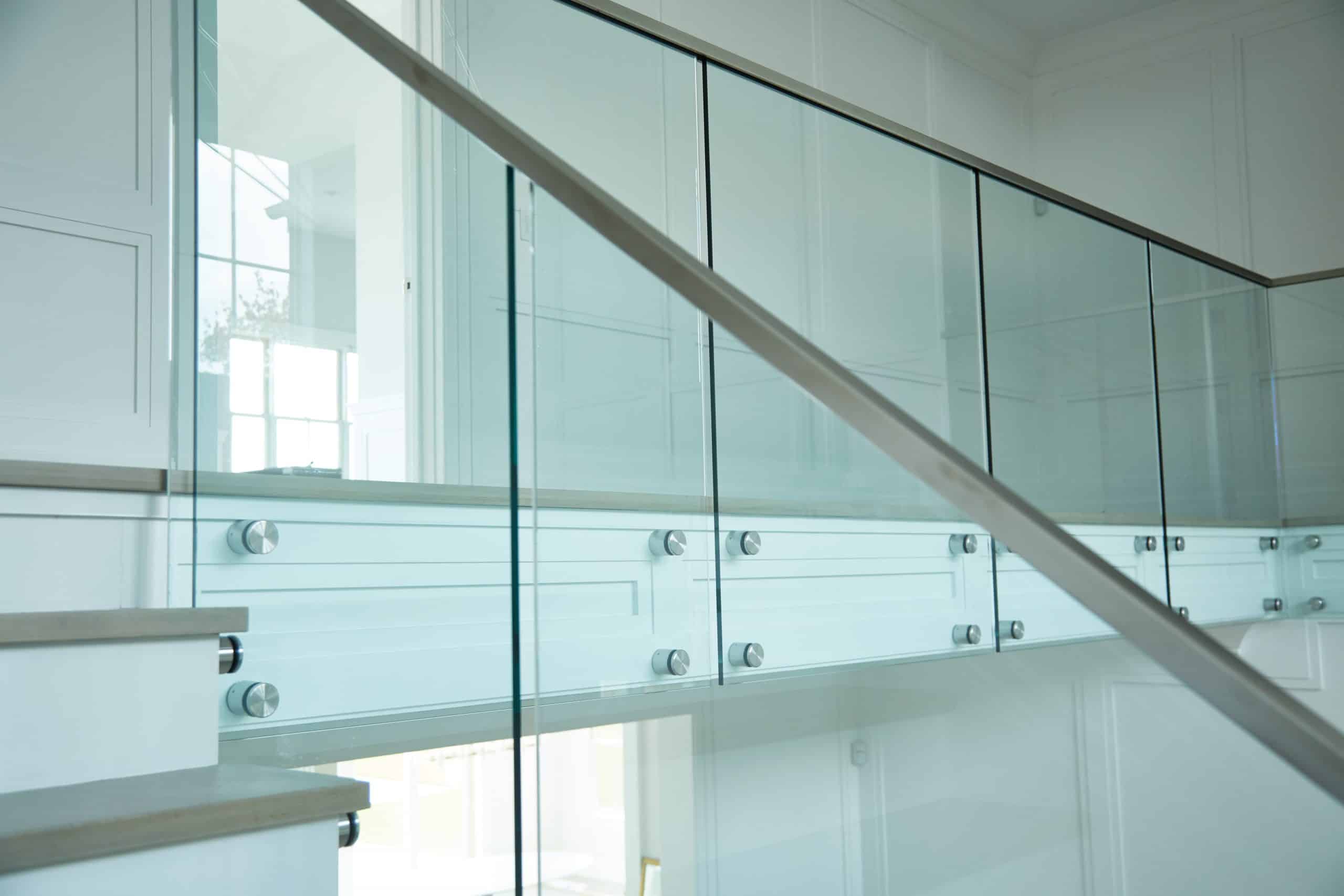
Glass Balustrades are an aesthetically pleasing and versatile feature in the commercial glass and aluminum industry.
Glass Railing has stunning visual impact, adds openness, makes spaces feel bigger and facilitates light flow.
Glass Balustrades are an aesthetically pleasing and versatile feature in the commercial glass and aluminum industry.
Glass BalustradesGlass Balustrades are an aesthetically pleasing and versatile feature in the commercial glass and aluminum industry.
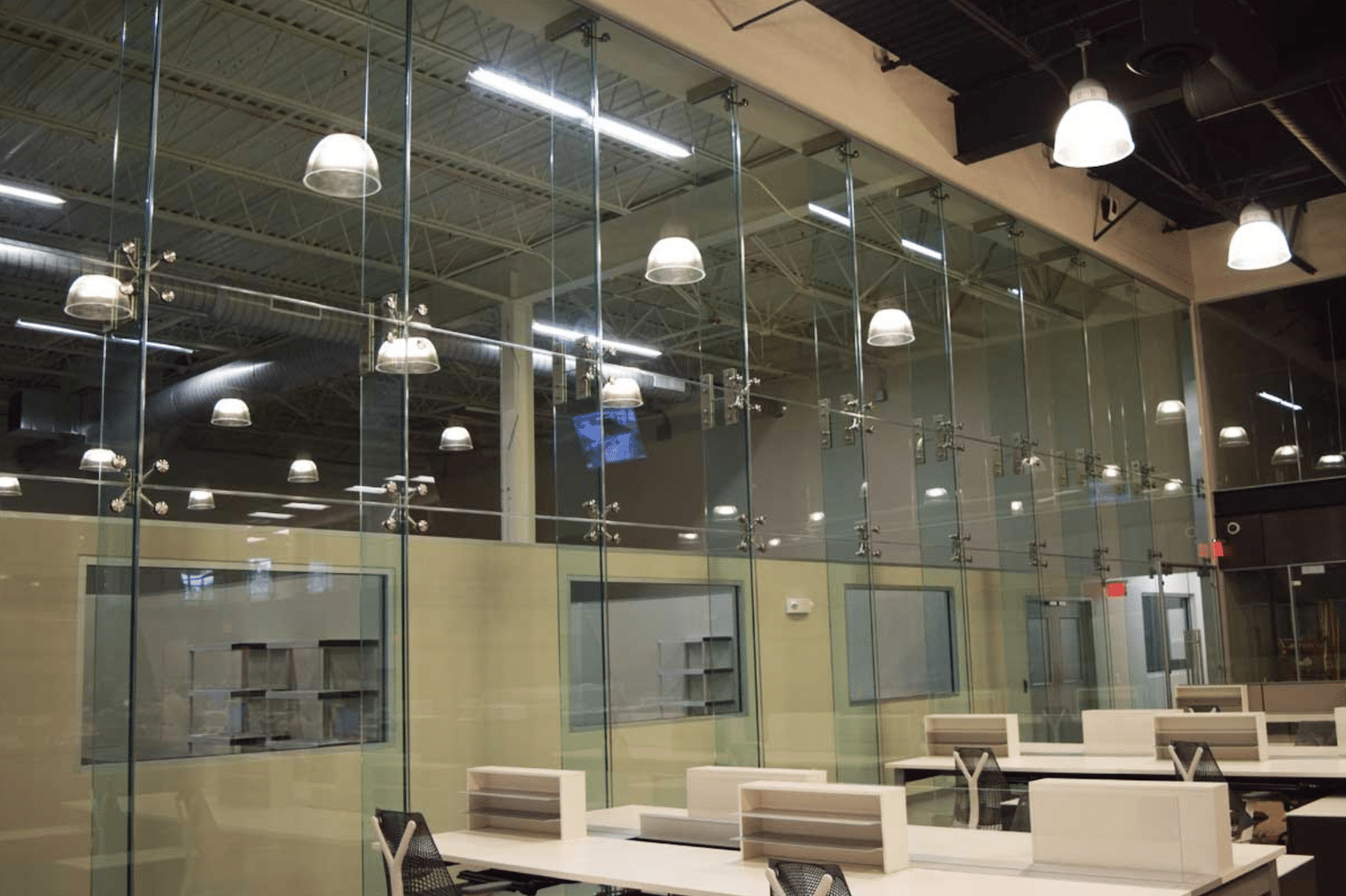
Point Supported Systems, key elements in façade engineering, offer a unique blend of frameless appearance and structural support.
We specialize in providing innovative and high-quality glazing solutions for commercial glass doors and windows.
Point Supported SystemPoint Supported Systems, key elements in façade engineering, offer a unique blend of frameless appearance and structural support.
- Window Films
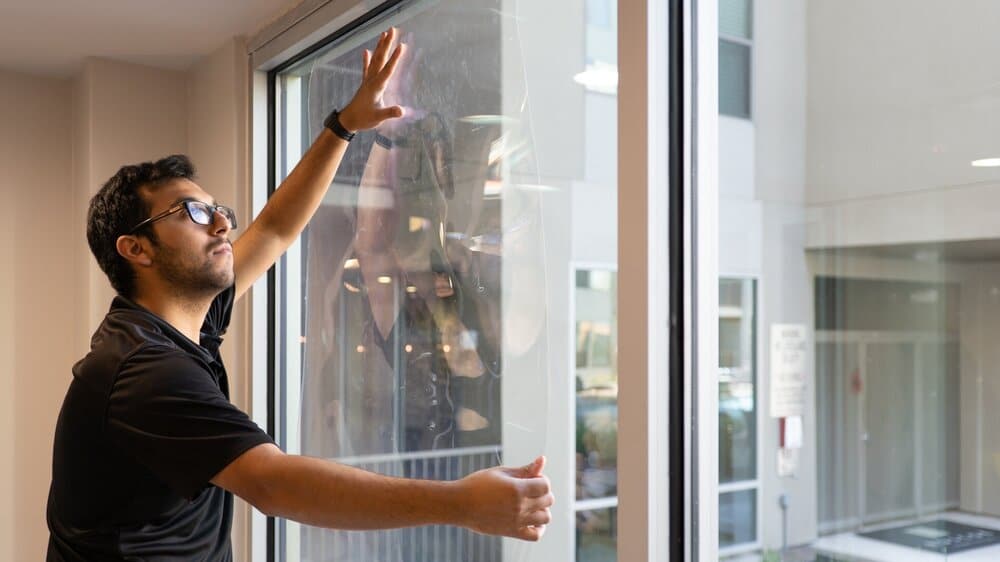
Window Films overview
- Applied Film Options
- Solutions
We offer a comprehensive range of security solutions through the application of films on glass systems.
Privacy Films provide confidentiality, security, or personal privacy.
At Unique Glass and Aluminum Solutions we specialize in the installation of security film.
Bullet-resistant glass film, also known as security or ballistic film.
Bird-friendly films are an innovative and responsible solution designed to protect our avian friends.
Vision strip films are a versatile and practical solution for enhancing privacy and aesthetics in commercial and architectural settings.
Electrified films offer a unique and versatile solution for transforming glass surfaces into dynamic and interactive elements.
The need for secretive films arises from the growing demand for spaces that require restricted visibility without compromising natural light transmission.
Security FilmsWe offer a comprehensive range of security solutions through the application of films on glass systems.
We offer a wide range of unique and distinctive glass options to transform your space into something truly extraordinary.
We offer a wide range of unique and distinctive glass options to transform your space into something truly extraordinary.
Specialty Glass OptionsWe offer a wide range of unique and distinctive glass options to transform your space into something truly extraordinary.
- Aluminum Systems
Aluminum Systems overview
- Storefront Systems
- Curtain Wall
- Door Systems
It is crucial to make a positive first impression and ensure that your storefront entry systems are not only visually appealing but also secure and functional.
Curtain walls are an integral part of our comprehensive range of aluminum door solutions.
Aluminum frames play a vital role in our comprehensive range of aluminum door solutions.
We excel in supplying custom-made glass and aluminium solutions that are adapted to your individual demands and objectives.
Sloped Glazing Skylights are a prominent and transformative feature in the commercial aluminum and glass industry.
Storefront SystemsIt is crucial to make a positive first impression and ensure that your storefront entry systems are not only visually appealing but also secure and functional.
Curtain walls are an integral part of our comprehensive range of aluminum door solutions.
Stick built curtain walls are constructed on-site, using individual components that are assembled and installed piece by piece.
Unitized curtain walls refer to a type of building facade system where the curtain wall panels are pre-fabricated and assembled into individual units in a factory-controlled environment.
Curtain WallCurtain walls are an integral part of our comprehensive range of aluminum door solutions.
Sliding doors also called Patio Doors can transform your area with a unique, modern twist.
Aluminum swing doors are a popular choice for both industrial, institutional and commercial applications.
Discover D8, your destination for a wide range of automatic revolving doors, designed to be visually appealing, adaptable, and highly secure.
Sliding DoorsSliding doors also called Patio Doors can transform your area with a unique, modern twist.
- Application
- FAQ
FAQ
- Types of Glass
- Glass Solutions
Fire Rated Glass are one of them.
Insulated glass, also known as double glazing, comprises two or more glass window panes separated by a vacuum or gas-filled space to reduce heat transfer.
Heat Strengthened is one of them.
Laminated glass is a safety glass made by sandwiching a layer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or other interlayer materials between two or more panes of glass.
Low E Glass is one of them.
Monolithic glass refers to a single layer of glass which hasn’t been modified or combined with any other materials.
Spandrel glass is a type of opaque or translucent glass used in parts of a building’s exterior facade.
Tempered Glass is one of them.
Fire-Rated GlassThere are various types of commercial glasses. Fire Rated Glass are one of them.
It hence, can be confusing to select the right option for your specific need.
Point Supported Glass Systems are one way is one of them.
Glass balustrade is a transparent, often frameless, safety barrier typically used in balconies, and staircases.
There are various types of commercial glasses. Sloped Glazing Solutions are one way is one of them.
Glazing SolutionsThere are various types of Glazing Solutions. It hence, can be confusing to select the right option for your specific need.